Note
Click here to download the full example code
Unconditional Image Generation With DDIM Model Tutorial¶
Author: Muhammed Ayman
"""
This is an Implementation for `Denoising Diffusion Implicit Models (DDIM) <https://arxiv.org/abs/2010.02502>`__
===============================================================================================================
DDIM is one of the denoising diffusion probabilistic models family but
the key difference here it doesn�t require **a large reverse diffusion
time steps** to produce samples or images.
"""
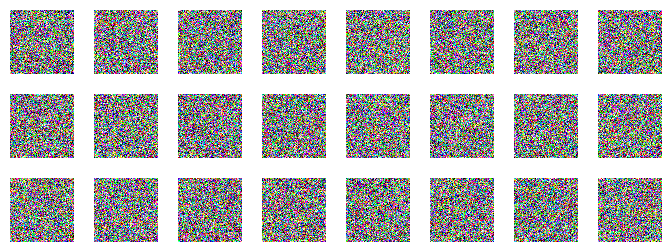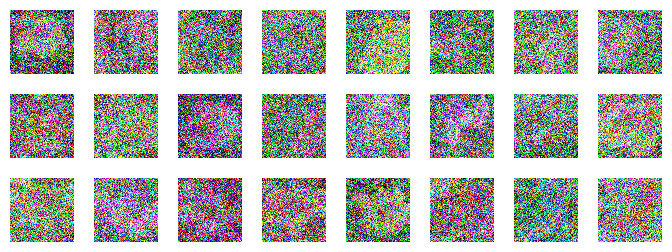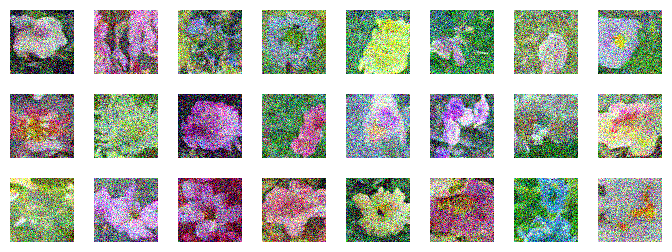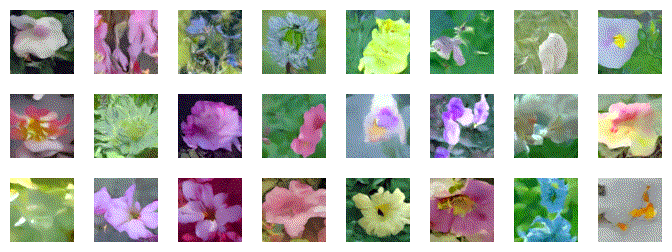
Setup
# =====
#
import torch
from torch import nn
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import torchvision.transforms.functional as F
from torchmetrics.image.kid import KernelInceptionDistance
from PIL import Image
Downloading Data and Preparing the pipeline
# ===========================================
#
Here We download the Oxford Flowers Dataset for generating images of
# flowers, which is a diverse natural flowers dataset containing around 8,000
# images with 102 category.
#
import torchvision.datasets as data
data.OxfordIIITPet('./data',download=True)
data.Flowers102("./data",download=True)
Here we prepare the data pipline using Dataset and Dataloader classes
# from **torch.utils.data** instance
#
from torch.utils.data import Dataset,DataLoader
from PIL import Image
from torchvision import transforms
class PetDataset(Dataset):
def __init__(self,pathes,img_size=(64,64),train=True):
self.pathes = pathes
self.img_size = img_size
self.aug = transforms.Compose([
transforms.RandomHorizontalFlip(),
# transforms.RandomAdjustSharpness(2)
])
self.processor = transforms.Compose(
[
transforms.Resize(self.img_size, antialias=True),
transforms.ToTensor(),
transforms.Normalize([0.5], [0.5]), # to normalize the images from [0,255] to [-1,1]
]
)
self.train = train
def _center_crop(self,img):
h,w = img.size
crop_size = min(h,w)
img = img.crop(((h-crop_size)//2,
(w-crop_size)//2,crop_size,crop_size))
return img
def __len__(self):
return len(self.pathes)
def __getitem__(self,idx):
img = Image.open(self.pathes[idx]).convert("RGB")
img = self._center_crop(img)
img = self.processor(img)
if self.train:
img = self.aug(img)
return img
import os
import random
all_flowers_pathes = [os.path.join('/content/data/flowers-102/jpg',x)for x in os.listdir('/content/data/flowers-102/jpg')
if x.endswith('.jpg')] # to gather all image pathes
random.shuffle(all_flowers_pathes)
train_pathes = all_flowers_pathes[:-500]
val_pathes = all_flowers_pathes[-500:]
train_ds = PetDataset(train_pathes) # training dataset
val_ds = PetDataset(val_pathes,train=False) # validation dataset
# helper function to display the image after generation
def display_img(img):
img = (img+1)*0.5
img= img.permute(1,2,0)
plt.imshow(img)
plt.axis('off')
test= val_ds[101] # grap a sample
display_img(test)
train_iter = DataLoader(train_ds,150,shuffle=True,num_workers=2,pin_memory=True)
val_iter = DataLoader(val_ds,20,num_workers=2,pin_memory=True)
Model Architecture and Modules
# ==============================
#
import math
MAX_FREQ = 1000
def get_timestep_embedding(timesteps, embedding_dim): # sinusoidal embedding like in Transformers
assert len(timesteps.shape) == 1
half_dim = embedding_dim // 2
emb = math.log(MAX_FREQ) / (half_dim - 1)
emb = torch.exp(torch.arange(half_dim, dtype=torch.float32) * -emb)
emb = emb.to(device=timesteps.device)
emb = timesteps.float()[:, None] * emb[None, :]
emb = torch.cat([torch.sin(emb), torch.cos(emb)], dim=1)
if embedding_dim % 2 == 1: # zero pad
emb = torch.nn.functional.pad(emb, (0, 1, 0, 0))
return emb
def Normalize(in_channels):
return torch.nn.GroupNorm(num_groups=32,
num_channels=in_channels,
eps=1e-6, affine=True)
def nonlinearity(name):
return getattr(nn,name)()
# Resnet Block
class ResidualBlock(nn.Module):
def __init__(self,in_chs,
out_chs,
temb_dim,
act='SiLU',dropout=0.2):
super().__init__()
self.time_proj = nn.Sequential(nonlinearity(act),
nn.Linear(temb_dim,out_chs))
dims = [in_chs]+2*[out_chs]
blocks =[]
for i in range(1,3):
blc = nn.Sequential(Normalize(dims[i-1]),
nonlinearity(act),
nn.Conv2d(dims[i-1],dims[i],3,padding=1),)
if i>1:
blc.insert(2,nn.Dropout(dropout))
blocks.append(blc)
self.blocks= nn.ModuleList(blocks)
self.short_cut = False
if in_chs!= out_chs:
self.short_cut = True
self.conv_short = nn.Conv2d(in_chs,out_chs,1)
def forward(self,x,temb):
h =x
for i,blc in enumerate(self.blocks):
h = blc(h)
if i==0:
h = h+self.time_proj(temb)[:,:,None,None]
if self.short_cut:
x = self.conv_short(x)
return x+h
# Attention Module
class AttnBlock(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, in_channels):
super().__init__()
self.in_channels = in_channels
self.norm = Normalize(in_channels)
self.q = torch.nn.Conv2d(in_channels,
in_channels,
kernel_size=1,
stride=1,
padding=0)
self.k = torch.nn.Conv2d(in_channels,
in_channels,
kernel_size=1,
stride=1,
padding=0)
self.v = torch.nn.Conv2d(in_channels,
in_channels,
kernel_size=1,
stride=1,
padding=0)
self.proj_out = torch.nn.Conv2d(in_channels,
in_channels,
kernel_size=1,
stride=1,
padding=0)
def forward(self, x):
h_ = x
h_ = self.norm(h_)
q = self.q(h_)
k = self.k(h_)
v = self.v(h_)
# compute attention
b, c, h, w = q.shape
q = q.reshape(b, c, h*w)
q = q.permute(0, 2, 1) # b,hw,c
k = k.reshape(b, c, h*w) # b,c,hw
w_ = torch.bmm(q, k) # b,hw,hw w[b,i,j]=sum_c q[b,i,c]k[b,c,j]
w_ = w_ * (c**(-0.5))
w_ = torch.nn.functional.softmax(w_, dim=2)
# attend to values
v = v.reshape(b, c, h*w)
w_ = w_.permute(0, 2, 1) # b,hw,hw (first hw of k, second of q)
# b, c,hw (hw of q) h_[b,c,j] = sum_i v[b,c,i] w_[b,i,j]
h_ = torch.bmm(v, w_)
h_ = h_.reshape(b, c, h, w)
h_ = self.proj_out(h_)
return x+h_
# Downsize Block
class DownBlock(nn.Module):
def __init__(self,
out_chs,
with_conv=True):
super().__init__()
self.with_conv = with_conv
if with_conv:
self.down_conv = nn.Conv2d(out_chs,out_chs,3,stride=2)
else:
self.down_conv = nn.AvgPool2d(2,2)
def _down(self,x):
if self.with_conv:
pad = (0,1,0,1) # to make the input shape equals to the output shape after convulotion op
x = torch.nn.functional.pad(x, pad, mode="constant", value=0)
x = self.down_conv(x)
else:
x = self.down_conv(x)
return x
def forward(self,x):
return self._down(x)
# Upsample BLock
class UpBlock(nn.Module):
def __init__(self,out_chs,
with_conv=True,
mode='nearest',):
super().__init__()
self.with_conv = with_conv
self.mode = mode
if with_conv:
self.up_conv = nn.Conv2d(out_chs,out_chs,3,padding=1)
def _up(self,x):
x = torch.nn.functional.interpolate(
x, scale_factor=2.0, mode=self.mode)
if self.with_conv:
x = self.up_conv(x)
return x
def forward(self,x):
return self._up(x)
#Unet Model
class DiffUnet(nn.Module):
def __init__(self,chs=32,
chs_mult=[2,2,4,4,8],
attn_res=[16,8,4],
block_depth=2,
act='SiLU',
temb_dim=256,
with_conv=True,
res=64,dropout=0.3):
super().__init__()
self.chs = chs
self.conv_in = nn.Conv2d(3,chs,3,padding=1)
self.time_proj = nn.Sequential(nn.Linear(chs,temb_dim),
nonlinearity(act),
nn.Linear(temb_dim,temb_dim))
chs_mult = [1]+chs_mult
#down block
down_dims = [] # to store the down features
downs = [] # to store the down blocks of the unet model
for i in range(1,len(chs_mult)-1):
in_ch = chs*chs_mult[i-1]
out_ch = chs*chs_mult[i]
down = nn.Module()
down.res = nn.ModuleList([ResidualBlock(in_ch,out_ch,temb_dim,act,dropout)]+
[ResidualBlock(out_ch,out_ch,temb_dim,act,dropout) for _ in range(1,block_depth)])
attn = AttnBlock(out_ch) if res in attn_res else nn.Identity()
down.attn = attn
down.down_blc = DownBlock(out_ch,with_conv)
downs.append(down)
down_dims.append(out_ch)
res = res//2
self.downs = nn.ModuleList(downs)
#mid block
last_ch_dim= chs*chs_mult[-1]
self.mid_res1 = ResidualBlock(out_ch,
last_ch_dim,
temb_dim,act,dropout)
self.mid_attn = AttnBlock(last_ch_dim)
self.mid_res2 = ResidualBlock(last_ch_dim,
last_ch_dim,
temb_dim,act,dropout)
#up block
down_dims = down_dims[1:]+[last_ch_dim]
ups = []
for i,skip_ch in zip(reversed(range(1,len(chs_mult)-1)),reversed(down_dims)):
out_ch = chs*chs_mult[i]
in_ch = out_ch+skip_ch
up = nn.Module()
up.res = nn.ModuleList([ResidualBlock(in_ch,out_ch,temb_dim,act,dropout)]+
[ResidualBlock(out_ch*2,out_ch,temb_dim,act,dropout) for _ in range(1,block_depth)])
attn = AttnBlock(out_ch) if res in attn_res else nn.Identity()
up.attn = attn
up.up_blc = UpBlock(skip_ch,with_conv) if i!=0 else nn.Identity()
ups.append(up)
res = int(res*2)
self.ups = nn.ModuleList(ups)
self.out = nn.Sequential(Normalize(out_ch),
nonlinearity(act),
nn.Conv2d(out_ch,3,3,padding=1))
self.res = res
def forward(self,x,timestep):
t = get_timestep_embedding(timestep,self.chs)
t = self.time_proj(t)
h = self.conv_in(x)
hs =[]
#Down
for blc in self.downs:
for res_block in blc.res:
h = res_block(h,t)
h = blc.attn(h)
hs.append(h)
h = blc.down_blc(h)
#Mid
h = self.mid_res1(h,t)
h = self.mid_attn(h)
h = self.mid_res2(h,t)
#Up
for blc in self.ups:
h = blc.up_blc(h)
for res_block in blc.res:
h = torch.cat([h,hs.pop()],axis=1)
h = res_block(h,t)
h = blc.attn(h)
return self.out(h)
Diffusion Model and noise scheduler
# ===================================
#
import math
import numpy as np
from typing import Optional, Tuple, List,Union
def get_beta_schedule(beta_schedule, *, beta_start, beta_end, num_diffusion_timesteps):
def sigmoid(x):
return 1 / (np.exp(-x) + 1)
def alpha_bar(time_step):
return math.cos((time_step + 0.008) / 1.008 * math.pi / 2) ** 2
if beta_schedule == "quad":
betas = (
np.linspace(
beta_start ** 0.5,
beta_end ** 0.5,
num_diffusion_timesteps,
dtype=np.float32,
)
** 2
)
elif beta_schedule == "linear":
betas = np.linspace(
beta_start, beta_end, num_diffusion_timesteps, dtype=np.float64
)
elif beta_schedule == "sigmoid":
betas = np.linspace(-6, 6, num_diffusion_timesteps)
betas = sigmoid(betas) * (beta_end - beta_start) + beta_start
elif beta_schedule == "cosv2":
betas = []
for i in range(num_diffusion_timesteps):
t1 = i / num_diffusion_timesteps
t2 = (i + 1) / num_diffusion_timesteps
betas.append(min(1 - alpha_bar(t2) / alpha_bar(t1), beta_end))
betas = np.array(betas)
else:
raise NotImplementedError(beta_schedule)
assert betas.shape == (num_diffusion_timesteps,)
return betas
class DDIMSampler:
def __init__(self,
schedule_name: str,
diff_train_steps: int,
beta_start: float = 0.001,
beta_end: float = 0.2):
betas = get_beta_schedule(schedule_name,
beta_start=beta_start,
beta_end=beta_end,
num_diffusion_timesteps=diff_train_steps)
self.betas = torch.tensor(betas).to(torch.float32)
self.alpha = 1 - self.betas
self.alpha_cumprod = torch.cumprod(self.alpha, dim=0)
self.timesteps = np.arange(0, diff_train_steps)[::-1]
self.num_train_steps = diff_train_steps
self._num_inference_steps = 20
self.eta = 0
def _get_variance(self,
timestep: Union[torch.Tensor, int],
prev_timestep: Union[torch.Tensor, int] ):
alpha_t = self.alpha_cumprod[timestep]
alpha_prev = self.alpha_cumprod[prev_timestep] if prev_timestep >= 0 else torch.tensor(1.0)
beta_t = (1 - alpha_t)
beta_prev = (1 - alpha_prev)
return (beta_prev / beta_t) / (1 - alpha_t / alpha_prev)
@staticmethod
def treshold_sample(sample: torch.Tensor,
threshold: float = 0.9956,
max_clip: float = 1):
batch_size, channels, height, width = sample.shape
dtype = sample.dtype
if dtype not in (torch.float32, torch.float64):
sample = sample.float() # upcast for quantile calculation, and clamp not implemented for cpu half
# Flatten sample for doing quantile calculation along each image
sample = sample.reshape(batch_size, channels * height * width)
abs_sample = sample.abs() # "a certain percentile absolute pixel value"
s = torch.quantile(abs_sample, threshold, dim=1)
s = torch.clamp(
s, min=1, max=max_clip
) # When clamped to min=1, equivalent to standard clipping to [-1, 1]
s = s.unsqueeze(1) # (batch_size, 1) because clamp will broadcast along dim=0
sample = torch.clamp(sample, -s, s) / s # "we threshold xt0 to the range [-s, s] and then divide by s"
sample = sample.reshape(batch_size, channels, height, width)
sample = sample.to(dtype)
return sample
def set_infer_steps(self,
num_steps: int,
device: torch.DeviceObjType):
self._num_inference_steps = num_steps
step_ratio = self.num_train_steps // self._num_inference_steps
# creates integer timesteps by multiplying by ratio
# casting to int to avoid issues when num_inference_step is power of 3
timesteps = (np.arange(0, num_steps) * step_ratio).round()[::-1].copy().astype(np.int64)
self.timesteps = torch.from_numpy(timesteps).to(device)
@torch.no_grad()
def p_sample(self,
x_t: torch.Tensor,
t_now: Union[torch.Tensor, int],
pred_net):
prev_timestep = t_now - self.num_train_steps // self._num_inference_steps
alpha_t = self.alpha_cumprod[t_now]
alpha_prev = self.alpha_cumprod[prev_timestep] if prev_timestep >= 0 else torch.tensor(1.0)
var = self._get_variance(t_now, prev_timestep)
eps = torch.randn_like(x_t).to(x_t.device)
t_now = (torch.ones((x_t.shape[0],),
device=x_t.device,
dtype=torch.int32) * t_now).to(x_t.device)
eta_t = pred_net(x_t, t_now)
x0_t = (x_t - eta_t * (1 - alpha_t).sqrt()) / alpha_t.sqrt()
c1 = self.eta * var.sqrt()
c2 = ((1 - alpha_prev) - c1 ** 2).sqrt()
x_tminus = alpha_prev.sqrt() * x0_t + c2 * eta_t + c1 * eps
return x_tminus, x0_t
def q_sample(self,
x_t: torch.Tensor,
timesteps: Union[torch.Tensor, int]):
alpha_t = self.alpha_cumprod[timesteps].to(timesteps.device)
alpha_t = alpha_t.flatten().to(x_t.device)[:, None, None, None]
eps = torch.randn(*list(x_t.shape)).to(x_t.device)
x_t = alpha_t.sqrt() * x_t + (1 - alpha_t).sqrt() * eps
return x_t, eps
import copy
class DiffusionModel:
def __init__(self,
main_net: DiffUnet,
ema_net: Optional[DiffUnet] = None,
num_steps: int = 100,
input_res: Union[Tuple[int, int], List[int]] = (32, 32),
emma: float = 0.999,
noise_sch_name: str = 'cosv2',
**noise_sch_kwargs):
self.device = torch.device('cuda' if torch.cuda.is_available() else 'cpu')
self.eps_net = main_net.to(self.device)
self.ema_net = ema_net if ema_net is not None else copy.deepcopy(main_net)
self.ema_net = self.ema_net.to(self.device)
self.ema_net.eval()
self.steps = num_steps
self.res = (3,) + input_res if isinstance(input_res, tuple) else [3] + input_res
self.num_steps = num_steps
self.scheduler = DDIMSampler(noise_sch_name,
diff_train_steps=num_steps,
**noise_sch_kwargs)
self.emma = emma
@torch.no_grad()
def generate(self,
num_samples: int = 1,
num_infer_steps: int = 25,
pred_net: Optional[str] = 'ema',
return_list: bool = False,
x_t: Optional[torch.Tensor] = None):
shape = (num_samples,) + self.res if isinstance(self.res, tuple) else [num_samples] + self.res
x_t = torch.randn(*shape).to(self.device) if x_t is None else x_t
self.scheduler.set_infer_steps(num_infer_steps, x_t.device)
pred_net = getattr(self, pred_net + "_net")
xs = [x_t.cpu()]
for step in range(num_infer_steps):
t = self.scheduler.timesteps[step]
x_t, _ = self.scheduler.p_sample(x_t, t, pred_net)
xs.append(x_t.cpu())
return xs[-1] if not return_list else xs
@staticmethod
def inverse_transform(img):
""" Inverse transform the images after generation"""
img = (img + 1) / 2
img = np.clip(img, 0.0, 1.0)
img = np.transpose(img, (1, 2, 0)) if len(img.shape) == 3 else np.transpose(img, (0, 2, 3, 1))
return img
@staticmethod
def transform(img):
"""Transform the image before training converting the pixels values from [0, 255] to [-1, 1]"""
img = img.to(torch.float32) / 127.5
img = img - 1
if len(img.shape) == 3: # one sample
img = torch.permute(img, (2, 0, 1))
else: # batch of samples
img = torch.permute(img, (0, 3, 1, 2))
return img
def train_loss(self,
input_batch: torch.Tensor,
loss_type: Optional[str] = 'l1_loss',
**losskwargs):
"""Training loss"""
bs, _, _, _ = input_batch.shape
t = torch.randint(0, self.num_steps, size=(bs,))
x_t, eps = self.scheduler.q_sample(input_batch, t)
t = t.int().to(input_batch.device)
eps_pred = self.eps_net(x_t, t)
loss = getattr(torch.nn.functional, loss_type)(eps_pred, eps, **losskwargs)
return loss
def update_emma(self):
for p_ema, p in zip(self.ema_net.parameters(), self.eps_net.parameters()):
p_ema.data = (1 - self.emma) * p.data + p_ema.data * self.emma
def train(self):
self.eps_net.train()
def eval(self):
self.eps_net.eval()
def parameters(self):
return self.eps_net.parameters()
def save(self,
file_name: str):
if not os.path.exists(file_name):
os.makedirs(file_name)
ema_path = file_name + '/ema.pt'
net_path = file_name + "/eps.pt"
torch.save(self.ema_net.state_dict(), ema_path)
torch.save(self.eps_net.state_dict(), net_path)
def load(self,
path_nets: str):
pathes = [os.path.join(path_nets, p) for p in os.listdir(path_nets) if ("ema" in p or "eps" in p)]
for index in range(len(pathes)):
if "ema" in pathes[index]:
break
ema_p = pathes[index]
eps_p = pathes[int(not index)]
map_loc = 'cpu' if not torch.cuda.is_available() else 'cuda'
self.eps_net.load_state_dict(torch.load(eps_p, map_location=map_loc))
self.ema_net.load_state_dict(torch.load(ema_p, map_location=map_loc))
DEVICE = torch.device('cuda' if torch.cuda.is_available()else 'cpu')
Unet = DiffUnet(block_depth=2)
Unet = Unet.to(DEVICE)
Model = DiffusionModel(Unet,num_steps=1000,input_res=(64,64))
optim = torch.optim.AdamW(Unet.parameters(),5e-4,weight_decay=0.01)
print("number of parameters:{}".format(sum([p.numel()for p in Unet.parameters()])))
kid = KernelInceptionDistance(subset_size=100,normalize=True).to(DEVICE)
# preprocess the data before KID
def prepare_kid(real,pred):
real = F.resize(((real+1)*0.5).clamp(0,1),(299,299))
pred = F.resize(((pred+1)*0.5).clamp(0,1),(299,299))
return real,pred
#Trainig utilities
#
mean = lambda x:sum(x)/len(x)
def mul(args):
res = 1
for i in args:
res*=i
return res
def train_epoch(model,train_ds,opt,loss_type='mse_loss',num=5,max_norm=None,**kwargs):
model.train()
losses = []
for i,inputs in enumerate(train_ds):
inputs = inputs.to(DEVICE)
opt.zero_grad()
loss = model.train_loss(inputs,loss_type,**kwargs)
loss.backward()
if max_norm is not None:
torch.nn.utils.clip_grad_norm_(model.parameters(), max_norm)
opt.step()
loss = loss.item()
losses.append(loss)
model.update_emma()
if (i+1)%(len(train_ds)//num)==0:
print(f"Finished training on {100*(i+1)/len(train_ds):.1f}% of the dataset and loss:{loss:.3f}")
return mean(losses)
def plot_grid_images(imgs,grid_shape):
n_rows,n_cols = grid_shape
plt.figure(figsize=(n_cols * 2, n_rows * 2))
plt.title('Generated Images')
for row in range(n_rows):
for col in range(n_cols):
index = row * n_cols + col
plt.subplot(n_rows, n_cols, index + 1)
img = imgs[index]
img = (img+1)/2
img= img.permute(1,2,0)
img = torch.clamp(img,0.0,1.0)
plt.imshow(img)
plt.axis('off')
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()
plt.close()
def val_epoch(model,val_ds,loss_type='mse_loss',grid_shape=[2,3],infer_steps=20,**kwargs):
model.eval()
with torch.no_grad():
losses = []
for i,inputs in enumerate(val_ds):
inputs = inputs.to(DEVICE)
loss = model.train_loss(inputs,loss_type,**kwargs)
loss = loss.item()
losses.append(loss)
samples = model.generate(int(inputs.shape[0]),infer_steps).cuda()
inputs ,samples = prepare_kid(inputs,samples)
kid.update(inputs,real=True)
kid.update(samples,real=False)
mean_kid,std_kid = kid.compute()
kid.reset()
return mean(losses),mean_kid,std_kid
Training Loop
# =============
#
import time
EPOCHS = 10
loss_type='l1_loss'
max_kid= 0.5
path_to_save = '/content/Pretrained/DDIM'
for e in range(EPOCHS):
st = time.time()
print(f"Started Training on:{e+1}/{EPOCHS}")
train_loss = train_epoch(Model,train_iter,optim,loss_type,max_norm=1.0)
val_loss,mean_kid,std_kid = val_epoch(Model,val_iter,loss_type)
if mean_kid<max_kid:
path = path_to_save+f"{mean_kid:.2f}_model" # the weights name includes the kid score to make it easy to identify the best weights
Model.save(path)
max_kid = mean_kid
print(f"Finished Training on epoch: {e+1} in {(time.time()-st)/60:.1f} mins, train_loss: {train_loss:.3f},val_loss:{val_loss:.3f},kid(mean={mean_kid:.3f},std={std_kid:.3f})\n")
Generation Time!
# ================
#
# load the best parameters
Model.load("/content/Pretrained/Pretrained/0.05_model") # put the path to the weights directory here
num_samples = 24
x = torch.randn(num_samples,3,64,64).cuda()
# if you want the images for througout the genration process you should make the return list attribute True
emma_samples = Model.generate(num_infer_steps=25,x_t=x)
samples = [sam.squeeze() for sam in emma_samples][-24:]
plot_grid_images(samples,[3,8])
# Make a grid from a set of images
def make_grid(images,
padding=10,
grid_sh=(2,10),
color=(255,255,255)):
rows,cols = grid_sh
color = np.array(color,dtype=np.uint8)
imgs_h = []
for row in range(rows):
imgs_w =[]
for col in range(cols):
idx = row * cols + col
img= images[idx]
sh = np.array(img.shape)+2*padding # padding for seperating the images in the grid
sh[-1] = img.shape[-1]
new_img = np.ones(sh,dtype=np.uint8)*color[None,None,:]
new_img[padding:sh[0]-padding,padding:sh[1]-padding,:] = img
imgs_w.append(new_img)
new_img = np.concatenate(imgs_w,axis=1)
imgs_h.append(new_img)
return np.concatenate(imgs_h)
# inverse data transform
def inverse(img):
img = (img+1)/2
img = (np.clip(img,0.0,1.0)*255).astype(np.uint8)
img = np.transpose(img,(0,2,3,1)) if len(img.shape)==4 else np.transpose(img,(1,2,0))
return img
IMGS = Model.generate(24,25,return_list=True)
IMGS = [im.cpu().numpy() for im in IMGS]
# making a Gif to visualize the generation process
def make_gif(imgs,name='test',time=250):
imgs = [Image.fromarray(im) for im in imgs]
imgs[0].save(name+".gif", format="GIF", append_images=imgs,
save_all=True, duration=time, loop=0)
IMGS = [make_grid(inverse(ims),grid_sh=(3,8)) for ims in IMGS]
IMGS += [IMGS[-1]]*10
make_gif(IMGS)
Conclusion¶
That’s all for this one, folks. Congratulations, you now know the fundamentals to building a generative model! If you’re interested, you can try and build the conditional version where you generate images based on class inputs by tweaking the (model unet and resnet blocks)<https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/blob/main/src/diffusers/models/unet_2d_condition.py> and retrain the model.
Check out the other tutorials for more cool deep learning applications in PyTorch!
Total running time of the script: ( 0 minutes 0.000 seconds)



